Are you looking for an essay on the ‘Balance Sheet of a Bank’? Find paragraphs, long and short essays on the ‘Balance Sheet of a Bank’ especially written for school and banking students.
Essay on the Balance Sheet of a Bank
Essay Contents:
- Essay on the Introduction to Balance Sheet of a Bank
- Essay on the Features (Characteristics) of New FORM of Balance Sheet of Bank
- Essay on the Detailed Description of Liabilities Side Items
- Essay on the Detailed Description of Asset Side Items
- Essay on the Items to be Shown as Notes at the End of Balance Sheet
- Essay on the Advantages of Balance Sheet of Bank
Essay # 1. Introduction to the Balance Sheet of a Bank:
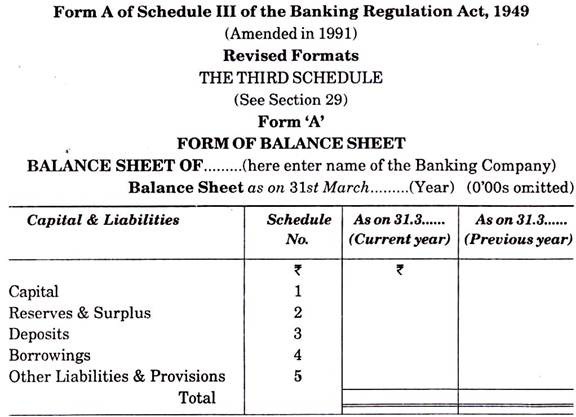
Banking Companies are governed by the Banking Regulation Act, 1949. As per section 29 of Banking Regulation Act, 1949; every banking company is mandatory required to prepare Profit & Loss Account and Balance Sheet at the end of each year. Form of Profit & Loss Account and Balance Sheet is given in schedule III of Banking Regulation Act, 1949.
Before 1992 Profit & Loss Account and Balance Sheet of a bank was published in old format. To remove the defects 6f old format a committee was formed by the Central Government under the chairmanship of A. K. Ghosh on the basis of the rights of Banking Regulation Act, 1949.
On the recommendation of the above said committee a circular was issued by Reserve Bank of India for all the commercial banks except the Regional Rural Banks to prepare Profit & Loss Account and Balance Sheet by banks in new format is made mandatory from 31st March, 1992. New forms are vertical in which, all data is to be presented with the help of schedules. 12 schedules are related to Balance Sheet while 4 schedules are related to Profit & Loss Account and 2 schedules for accounting policies. Thus, total 18 schedules are to be used.
Essay # 2. Features (Characteristics) of New FORM of Balance Sheet of Bank:
The main characteristics of new form of Balance Sheet of bank are as follows:
1. In new format of Balance Sheet only the main heading are written.
2. The details of the main headings are shown separately in schedules.
3. In new format amount is shown in ‘thousand rupees’; while in old format it was shown upto in ‘paise’.
4. In revised format new headings are given in place of old headings.
5. In new format of Balance Sheet amount of current year can be compared with the amount of previous year at a glance.
Essay # 3. Detailed Description of Liabilities Side Items:
Detailed descriptions of the items of liabilities side are as follows:
1. Capital:
In Balance Sheet capital is written on the basis of the description of schedule-1. For this, banks are classified in three categories-Nationalised banks, banks incorporated outside India and other banks.
(a) For nationalised banks it is necessary to explain to at total capital is held by the central Government.
(b) In case of a bank incorporated outside India, following two amounts are to written in relation to capital:
(i) Capital defined by RBI which has been brought by the bank.
(ii) Amount deposited with RBI as per Sec. 11 (2) of Banking Regulation Act, 1949.
Aggregate of (i) and (ii) is to be shown.
(c) Capital of other banks is to be shown as Authorised capital, issued capital, subscribed capital, called up and paid up capital separately. Calls in arrears are to be deducted and amount of forfeited shares is to be added to the amount of called up capital.
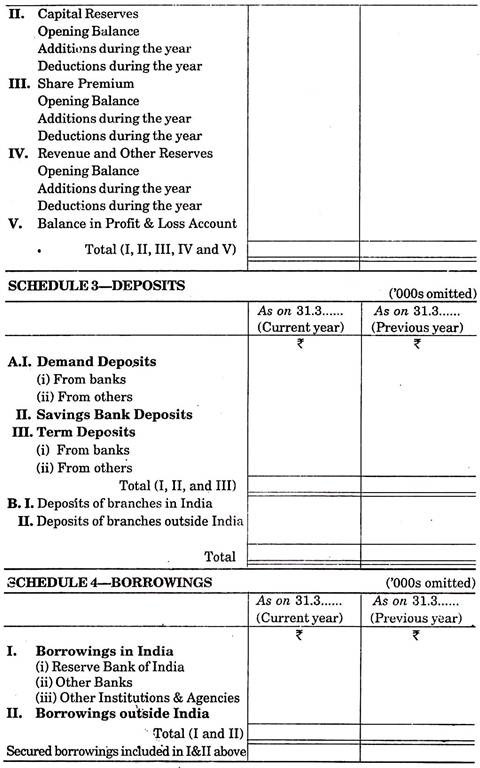
2. Reserves and Surplus:
The detail of Reserve and Surplus is given in schedule-2 of Balance Sheet.
It is classified into five subheadings:
(a) Statutory Reserve:
Statutory Reserve is that reserve which is mandatory as per law. According to section 17 of banking regulation Act., 1949 every bank has to transfer 20 per cent portion of the net profit of current year in this reserve until and unless it reaches equal to the amount of paid up capital.
(b) Capital Reserve:
Capital Reserve is generally created on the profit of revaluation of assets. No dividend can be distributed out of capital reserve.
(c) Security Premium:
When the shares are issued by the bank in primary market, the amount of security premium is written in a separate subheading, which is a part of reserve and surplus.
(d) Revenue and other Reserves:
In addition to statutory reserves and capital reserve, many reserves are created by the banks for example- General Reserve, Dividend Equalisation Reserve, Fluctuation Reserve etc. These are written under this sub-heading.
(e) Balance in Profit & Loss Account:
After transferring the above reserves out of net profit remaining amount is written under this sub-heading.
3. Deposits:
Deposits are written according to schedule-3. Deposits repayable on demand, deposits in saving bank account, term deposits etc.
Eire to be shown separately under the headings of:
(a) Demand deposits,
(b) Saving Bank Deposits, and
(c) Term deposits.
Demand deposits and Term deposits are subdivided as ‘from bank’ and ‘from others’.
Aggregate arrived at above is to be further sub-divided into two parts:
(i) Deposits of branches in India, and
(ii) Deposits of branches outside India.
4. Borrowings:
Amount borrowed by bank is to be shown under schedule-4. There are two sub-headings written in this heading. Under first subheading loans taken from Reserve Bank of India, from other banks and from other institutions and agencies are written; while in second sub-heading amount borrowed from outside India is written.
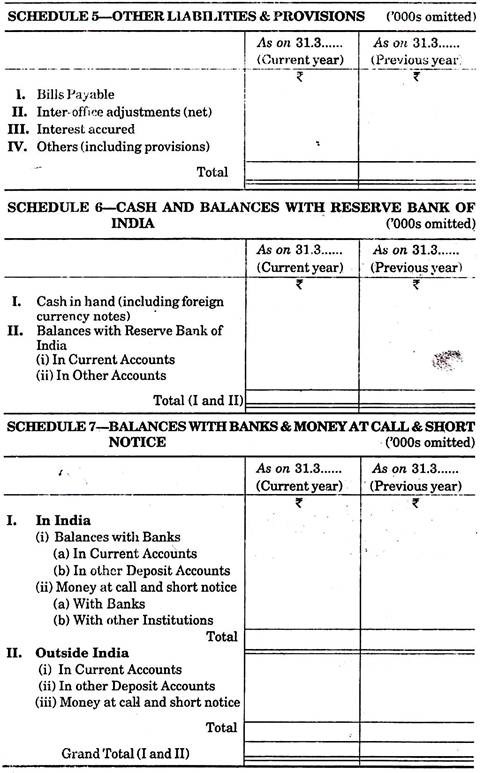
5. Other Liabilities and Provisions:
This is the last item of the liabilities side of Balance Sheet. It is shown under schedule-5. Under this heading bills payable, Inter-branch adjustment, Accrued interest and others (including provisions) are written.
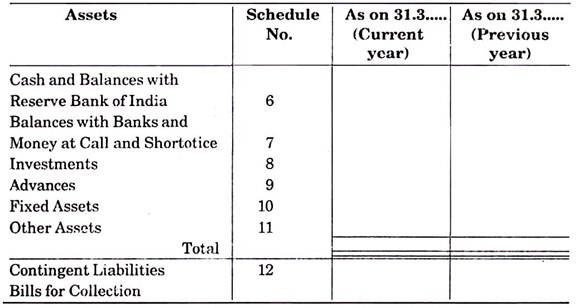
Essay # 4. Detailed Description of Asset Side Items:
Following items are written in the asset side of balance sheet:
1. Cash and Balances with Reserve Bank of India:
It is the first item of the asset side of the Balance sheet. It is shown in schedule-6.
Under this heading there are two sub-headings:
(i) Cash in hand (including foreign currency note), and
(ii) Balances with Reserve Bank of India in Current accounts and other accounts.
2. Balance with Banks and Money at Call and Short Notice:
This item is shown under schedule-7.
Following items are to be included in this schedule:
(i) Amount, deposited in current accounts and other accounts in India.
(ii) Money at call and short notice with banks or other institutions.
(iii) Amounts deposited and money at call and short notice with current accounts and other accounts outside India.
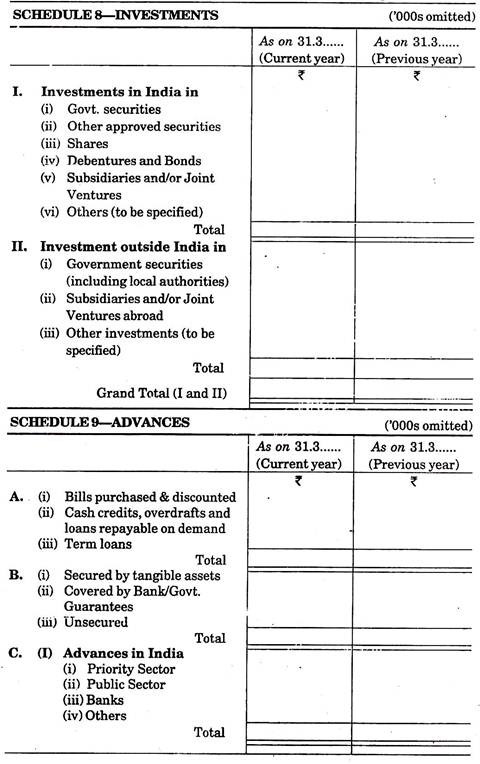
3. Investment:
Investment is shown in schedule-8. It is an important asset for a bank. It may be inside India and outside India. So, it is shown in two separate sub-headings. It includes investment in government or non-government securities like shares, debenture, bonds and others.
4. Advances:
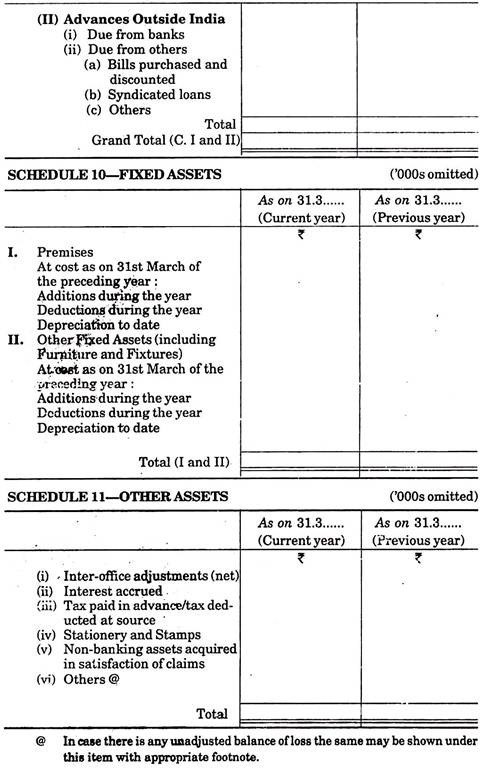
Detail of this heading is shown in schedule-9. Advances can be given in many ways for example-purchase or discounting of bills, cash credit, overdraft, loans repayable on demand term loans etc.
It is also necessary to explain how many amounts are secured by assets, how many amounts are secured by banks or government securities and how many amounts are unsecured. Further advances are also to be classified as provided in India and outside India.
5. Fixed Assets:
Detail of fixed asset is shown in schedule-10. Under this heading there are two sub-headings-firsts for premises and second for other assets. Additions, deductions and depreciation to date are also to be shown along with fixed assets.
6. Other Assets:
Assets which do not take place under above schedule are to be included under this head as per schedule-11.
Following items are written under this heading:
(i) Inter office/branch adjustments (net),
(ii) Accrued interest,
(iii) Tax paid in advance/tax deducted at source,
(iv) Stationery and stamp in stock,
(v) None banking assets in satisfaction of claims, and
(vi) Others (loss, if any, which are not written off, are to be shown under others).
Essay # 5. Items to be Shown as Notes at the End of the Balance Sheet:
Following two items are shown as notes at the end of the Balance Sheet:
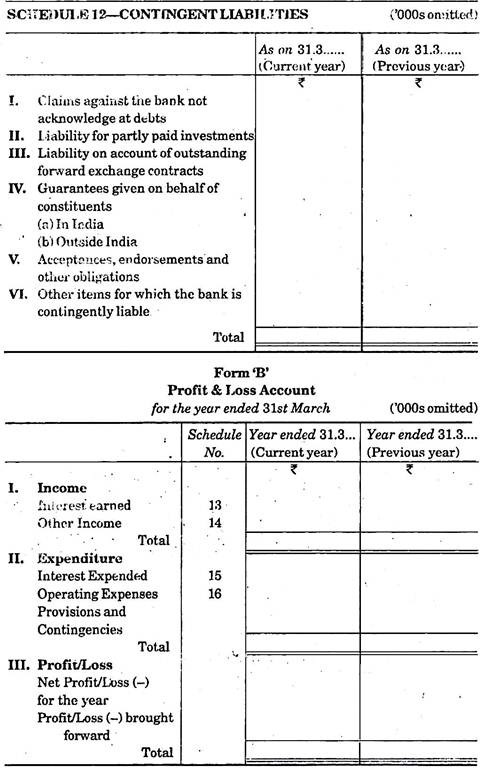
1. Contingent Liabilities:
It means the liability which arises on happening of a specific event. This is purely estimated or contingent whose happening is not definite. But in near future it may be a liability. So it is shown at the end of the balance sheet, as per schedule-12.
Following items are to be included under this heading:
(i) Claims against the bank not acknowledge at debts.
(ii) Liability for partly paid investments.
(iii) Liability on account of outstanding forward exchange contracts.
(iv) Guarantees given on behalf of constituents.
(v) Acceptance, endorsement and other obligations.
(vi) Other items for which and bank is contingently liable.
2. Bills for Collection:
These bills are only to be written for information at the end of the Balance Sheet. It is not to be included in assets or liabilities. No separate schedule is there for this item.
Essay # 6. Advantages of Balance Sheet of Bank:
Main advantages of balance sheet of bank are as follows:
1. Knowledge about Financial Position:
Balance Sheet of a bank is a mirror of economic position. It reflects the knowledge of financial position and working capital.
2. Knowledge about Progress:
Progress of bank can be known with the comparison of the Balance Sheet of previous year.
3. Comparison with Other Banks:
This is the age of competition. The Balance Sheet of banks is published. So any bank can compare the Balance Sheet with that of other bank.
4. Public Confidence:
The public confidence increases after the publication of Balance Sheet. They feel their deposits to be in a safe position.
5. Knowledge about Safety and Liquidity:
Security of debts can be seen in Balance Sheet. Similarly out of total assets how much assets are in liquid position can be known.