Are you looking for an essay on ‘Banks in India’? Find paragraphs, long and short essays on ‘Banks in India’ especially written for school and banking students. Also learn about the development, importance and kinds of banks in India.
Essay on Banks in India
Essay Contents:
- Essay on Industrial Development Bank of India
- Essay on Industrial Credit and Investment Corporation of India-ICICI
- Essay on Industrial Finance Corporation of India
- Essay on Industrial Investment Bank of India
- Essay on Small Industries Development Bank of India (SIDBI)
- Essay on Export-Import Bank of India—EXIM Bank
Essay on Bank # 1. Industrial Development Bank of India:
Industrial Development Bank of India was set up as an associate organisation of the Reserve Bank of India on 1st July, 1964. The objective of its foundation was to establish co-ordination among various industrial financial institutions along with supplying the industrial finance. In 1975, an act was brought to separate IDBI from the RBI and on 16th February, 1976 it became an independent institution. A governing council consisting of 22 members was set up for its management.
So far as it’s financial resources are under consideration, these consist of money obtained from issuing shares, loans obtained from the central government, loan obtained from the Industrial Credit Fund of the RBI and money obtained from the bonds issued in the market. Its Authorised Capital was Rs. 200 crores in 1980.
Functions of IDBI:
IDBI has had a prominent place in the banking sector.
The main functions performed by it include these:
1. Refinance of Industrial Loans:
The IDBI plays an important role in arranging refinance for such industries which have already got loans from the commercial banks and any state level financial institution.
2. Bills Rediscounting Scheme:
The purchasing of machines etc., in industries is encouraged through this scheme. When the companies making industrial machines sell these machines to such industries, they prepare a bill. The discounting of these bills is done by the hanks after being accepted. Banks get the facility of the discounting of these bills through IDBI.
3. Seed Capital Scheme:
Under these schemes, those entrepreneurs get assistance that have all desired qualities to run industries but they lack capital. IDBI either gives direct assistance or provides indirect help through State Finance Corporations.
4. Development of Backward Areas:
IDBI conducts the survey of the economically backward areas. It also provides help to industrialists and state Financial Corporations for the development of these areas.
5. Promotion of Institute for Small Scale Industries:
Mahatma Gandhi had told that the development of India consists in the small scale and cottage industries. IDBI has encouraged the small scale Industries Development Fund and the National Equity Fund.
6. Commercial Banking:
The establishment of IDBI Bank in 1995 is to fulfill the objective of providing services like other commercial banks.
7. Other Functions:
Besides the above mentioned work, IDBI has shown interest in some work as well.
Some examples are:
(i) It has started work of share broking.
(ii) It also does the finance work for exports.
(iii) It provides assistance to other financial institutions by making contributions in their bonds and shares.
Progress of IDBI:
IDBI distributed a loan of Rs. 17,059.4 crores during 1999-2000. Its financial assistance for 2002-03 and 2003-04 were Rs. 6,292 crores and Rs. 5,473 crores respectively.
But it passed a special ordinance in December 2003 which came into action on 2nd July, 2004. Again from 11th October, 2004 it was converted into a scheduled bank. In other words, IDBI was merged with IDBI Bank. This bank is also a scheduled bank now according to the Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934.
Essay on Bank # 2. Industrial Credit and Investment Corporation of India-ICICI:
The experts of the World Bank had recommended the foundation of a separate corporation with the objective of providing assistance in the development of small and medium scale industries. In the light of this recommendation ICICI was set up as a private limited company in January, 1955.
ICICI has promoted the industrialisation in the country by providing medium and long term loans to small and medium scale industries.
According to a decision in January, 1997 Shipping Credit and Investment Company of India (SCICI) were merged with ICICI. Again in October, 2001 it was decided that ICICI should be merged with ICICI Bank on 30th March, 2002 and it was also recommended by the RBI. After this merging, it has not remained a development finance institution.
Essay on Bank # 3. Industrial Finance Corporation of India:
Industrial Finance Corporation of India (IFCI) is the first Development Financial Institution of India. It was founded by the government of India on 1st July, 1948.
There was a lacking of institutions making long term financial schemes for India, due to which the economic problem for the industrial sector was arising. So, the government of India took the decision of Industrial Finance Corporation of India for the industrial sector.
With the passage of time, the capital market developed in the country. The government realised in the beginning of 1990 that there is the need of more flexibility of the financial sector of the country. Then the government reorganized it in the form of a limited company according to the Indian Company Act on 1st July, 1993.
IFCI had been playing the full responsibility of making the industrial policies of the government successful before the foundation of ICICI (1956) and IDBI (1964).
Assistance by Corporation:
IFCI has helped in the development of following sectors through its assistance:
(i) Services sector like hotel, hospital etc.
(ii) The capital and intermediately industries like electronic, synthetic plastic, synthetic fibre and chemicals.
(iii) Creative sector like energy, telecommunication etc.
(iv) Consumer goods like clothes, paper, sugar industries etc.
(v) Infrastructure industries like cement, iron and steel, chemical fertilizers etc.
Financial Sources of the Corporation:
The share capital is the main among the capital sources of the corporation. Its authorised capital is Rs. 1,000 crores. Its paid up capital is Rs. 790 crores. It collects its financial sources by issuing debentures and bonds also. The corporation also arranges a reserve fund for strengthening its internal economic condition. It has the right of accepting public deposit upto a certain limit. Besides these, it can obtain loans for 90 days on the securities of the central and state government.
Management of Corporation:
The management of the corporation is done by a board of directors which has 12 members and a chairperson. The chairperson of the management board is also the president of these corporations. Among the 12 members of the managing board, 2 are nominated by the central government and 4 by IDBI Bank. Besides these, 2 members are from the representatives of the scheduled banks, 2 from LIC and other similar financial institutions and 2 other are representatives of the co-operative banks.
Criticism of Corporations:
The corporation has done much praise worthy work since its foundation, but then also it has faced criticisms from time to time.
The main points of criticisms are as follows:
(i) It has been a constant criticism against the corporation that it has centralised the economic strength of the country.
(ii) It has neglected the underdeveloped and poorly developed states.
(iii) It makes unnecessary delays in granting loans.
(iv) Its rates of interest are high.
(v) There is lack of flexibility in the working system of corporation.
(vi) It gives loans only to big industries.
(vii) It has not been able to make its reputation in the capital market.
Essay on Bank # 4. Industrial Investment Bank of India:
Industrial Investment Bank of India was set up on 12th April, 1971. Initially its name was Industrial Reconstruction Bank of India (IRCI). It was re-organised on 20th March, 1985 and renamed as Industrial Investment Bank of India (IRBI). Again on 6th March, 1997 a bill was presented in the Lok Sabha and its name was converted into Industrial Investment Bank of India Limited (IIBIL) and it started its operation as a company after being registered under the Indian Companies Act, 1956.
Its Authorised Capital is Rs. 1,000 crores. It is the first institution set up for the reconstruction of unhealthy ill and closed industrial units. It’s headquarter is in Kolkata. It is a Grade-I merchant banker registered with SEBI. It had sanctioned Rs. 2,412 crores for the sick and closed units during 2003-04 out of which 2,252 crores were distributed.
Essay on Bank # 5. Small Industries Development Bank of India (SIDBI):
Small Industries Development Bank of India (SIDBI) was founded on 2nd April, 1990 according to Small Industries Development Bank Act, 1989. Since its foundation, SIDBI has been seen as a leading institution for the development of small scale industries.
The main objectives of its foundation are as follows:
(i) Promoting small scale industries.
(ii) Making arrangement of finance for small scale industries.
(iii) Making co-ordination with the institutions having similar activities.
The Issued Capital of SIDBI is Rs. 450 crores which is divided in 45 crore shares of Rs. 10 each. It is worth mentioning here that SIDBI was established as its associate bank IDBI under its ownership. So the whole-sum of Rs. 450 crore was the subscribed capital of IDBI. When SIDBI was set up, 19.21 per cent was kept up by it and the remaining 80.79 per cent was transferred to organisations under the control of the Central government such as—banks and insurance companies.
Functions of SIDBI:
The important functions of SIDBI are as follows:
(i) Due to being an apex organisation of the small scale industries sector, SIDBI works as a network with banks and state level financial institutions.
(ii) SIDBI makes arrangement for the refinance for the loans obtained by the small scale industries.
(iii) SIDBI helps in the discounting and rediscounting of bills of the seller of machines to small scale industries.
(iv) It finds out the ultimate borrower of the small scale industries sector and helps him.
(vi) SIDBI performs the task of establishing co-ordinating among the financial institutions granting loans to the entrepreneurs of small scale industrial sector.
(vi) SIDBI has taken the initiative of the foundation of marketing sources as a scheme of finance scheme considering the delay in getting the amount obtained by selling the producers of small scale industries.
(vii) It has also started the loan activities for the leasing companies.
Progress of SIDBI:
SIDBI has developed as the foundation pillar for the development of small scale industries in its short life span. A loan of Rs. 8,224 crores was granted by SIDBI by the year 2003-04 out of which Rs. 4,413 crores were distributed in that period. A loan of Rs. 42,223 crores was sanctioned by it in the year 2010-11, out of which Rs. 38,824 crores were distributed.
According to the London Banker Survey conducted in May 2001, SIDBI ranks 25 and the 30 development banks across the world. The objective of SIDBI in the development of micro, small and medium enterprises is in such a way that these can create employment and also leaded to the balanced regional development.
Essay on Bank # 6. Export-Import Bank of India—EXIM Bank:
EXIM Bank was established in 1st January, 1982. The objective of its foundation was providing financial assistance to exporters and importers and establishing co-ordination in the work of those financial institutions which arrange finance for exports and imports of goods and services.
The Authorised capital of the EXIM Bank at the time of its foundation was Rs. 200 crorcs which was later raised to Rs. 500 crores and then in 1998 upto Rs 1,000 crores. Its paid up capital in 2001 was Rs. 550 crores.
The head office of the EXIM Bank is in Mumbai and one more has been opened in Delhi. Its foreign offices have been opened in Washington, Singapore, Abidjan and Budapest.
In 2008-09, in the 27th year of its foundation, the profit before tax of the EXIM Bank was Rs. 610 crores and profit after tax was Rs. 477 crores while its profit after tax in 2003-04 was only Rs. 229 crores. Net Profit during 2009-10 was Rs. 513 crore. The Capital Adequacy Ratio of the bank on 31st March, 2008 was 15.13 per cent which became 21.6 per cent on 31st March, 2011.
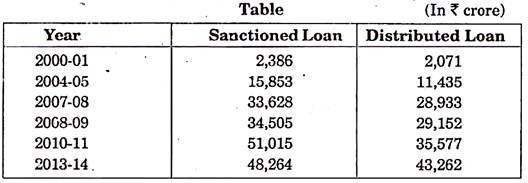
The sanctioned and distributed loans of the EXIM Bank can be clear by the following table: