After reading this essay you will learn about:- 1. Definitions of Decision Making 2. Procedure of Decision Making 3. Influence on Management 4. Biases 5. Guidelines 6. Modern Techniques 7. Current Trends 8. Group Decision Making.
Essay Contents:
- Essay on the Definitions of Decision Making
- Essay on the Procedure of Decision Making
- Essay on the Influence of Decision Making on Management
- Essay on the Biases in Decision Making
- Essay on the Guidelines for Decision Making
- Essay on the Modern Techniques for Decision Making
- Essay on the Current Trends of Decision Making
- Essay on Group Decision Making
Essay # 1. Definitions of Decision Making:
The main function of the management is to make decisions and to see that these are being carried out, not only in the starting of a concern but also in the course of running it. Problems may arise due to the change in the situations and due to other unforeseen circumstances during the course of production.
These problems can be solved through decision making for proper running of the concern. Such problems may be related to organisational structure, procedure, coordination, division of work and responsibility, deviation of quality standard, reduction in output etc.
“Decision Making” implies commitment to something, a point of a view, a principle, a course of action etc.
In other words, a decision is a course of action or inaction selected to meet the requirements of a solution to the problem.
“Decision Making” is an intellectual activity, because it calls for both judgment and imagination to select one from among many alternatives.
A “Decision” is something that takes place prior to the actual performance of the action that has been decided upon.
Decision making can also be defined as, an act of choice, wherein a manager forms a conclusion about what must be done under a given situation. A decision represents a course of behaviour chosen from a number of possible alternatives.
Essay # 2. Procedure of Decision Making:
Good decisions can only be made if following steps are taken before making decisions:
(i) Recognising and analysing the problems.
(ii) Finding relevant facts.
(iii) Determining possible alternatives.
(iv) Evaluating the impact of alternatives.
(v) Selecting the best solutions.
(vi) Implementation of the decisions.
(i) Recognising and analysing the problems:
The main job of manager is to find out the real problem before arriving at a decision. There may be a large number of symptoms that could be the real issue. Hence first step is to recognise and identify the real problem, and not simply the symptoms. It is just like a job of physician analysing all the symptoms before identifying the cause of illness.
For example, a manager notices a symptom of reduction in production. The problem is to find out why production is declining, whether it is due to reduction in the availability of raw material, power, or labour crisis, rising inefficiency in the plant or in employees.
To solve the difficult problems many managers normally break a problem into parts for easier diagnosis and solution. For this, generally different variables responsible for each part are found and seen whether it is controllable and if so than who will control and how it is to be controlled.
(ii) Finding relevant facts:
After recognising and analysing the problem next step is to collect all the relevant data. A decision must always be based on facts instead of guess and random thinking. As such, decision taken on the basis of facts, reduces the degree of uncertainty and risk. This also helps the managers to know the probable results of the decision.
(iii) Determining possible alternatives:
Generally problems have more than one alternatives and it is very rare that a problem has only one solution. To find out possible solutions manager has to keep an open mind, because he must consider all the possible solutions including a competitor’s solution or those used in the past.
After developing different alternatives next step in decision making is to evaluate the consequences of each proposed alternative.
(iv) Evaluating the impact of alternatives:
This is very important function of a decision maker, as decision depends very much on the skill and care used in evaluating each alternative.
After listing alternative solutions, decision maker must mentally put it into effect and visualise the impact of the alternatives and thus he forecasts what will happen if a certain alternative is adopted. While evaluating the impact of alternatives, manager must keep in mind all the limitations of the concern.
(v) Selecting the best solution:
Best solution is then selected by comparing the merits and demerits, gains or losses etc. of each alternative. Decision maker must also consider degree of risk, availability of resources, limitations and time required for implementation.
(vi) Implementation of Decisions:
After selecting a best solution, it is required to be converted into effective action. Actually manager makes the decision but he himself does not apply it. Hence the decision must be communicated to the persons applying it in a simple, clear and easily understandable language.
For better implementation, it is necessary that subordinates must feel sense of participation, for which they may be associated at some stage in decision making process. In the beginning, manager himself must take personal interest in implementing the decision.
Essay # 3. Influence of Decision Making on Management:
It is the proper decision which affects the efficiency, working and profitability of the concern. The management should take correct decisions at correct time. Sometimes this work becomes more complicated when there are more than one alternative solutions of a problem. Manager must be able to select one best alternative.
Some persons are of the opinion that capacity for making decision is a God gift and training cannot develop it in him, if he is not having this capacity originally. But others are of opinion that, of course good decision makers must be intelligent from the beginning but with practice, experience and training he can improve his decision -making ability and can become a very good manager.
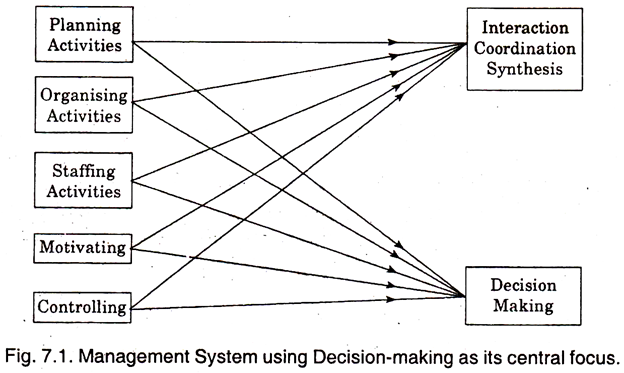
Fig. 7.1 explains the Management System using “Decision Making” as its central focus. The various sub systems are involved in different types of decisions but they do not act independently.
Essay # 4. Biases in Decision Making:
In human decision making most times, managers uses ‘heuristics’ i.e. the rules of thumb and use intuitive sense. But this leads to a number of biases.
Some of the most common biases are:
(i) Easy recall.
(ii) Easy search.
(iii) Overrating the importance of representative information.
(iv) Smaller size of the sample.
(v) Arriving at decisions by adjusting some initial values.
(vi) Over-confidential
Essay # 5. Guidelines for Effective Decision Making:
Following guidelines must be followed for effective decision making:
i. Define the goals.
ii. Ensure that decision will contribute to the goal.
iii. Involve subordinates in decision making process.
iv. Adopt a diagnostic and systematic approach.
v. Ensure implementation of the decision.
vi. Evaluate the results.
vii. Revise the decision on the basis of feedback.
Essay # 6. Modern Techniques for Decision Making:
In actual practice, all the Non-programmed decisions are made with some amount of uncertainty. However its degree may vary depending upon its extent of certainty and uncertainty. Thus there are certain risks involved in decision making.
There are number of modern techniques which can be used to improve are quality of decision- making under the normal conditions of uncertainty.
Among them most important are:
(i) Risk analysis,
(ii) Decision trees, and
(iii) Preference theory.
(i) Risk Analysis:
In risk analysis, decision maker wants to know the size and nature of risk involved in the decision, and degree of probability of success. Decision tree technique depicts the decision points, chance events, and probabilities involved in various courses that might be undertaken.
In preference or utility theory, preferences are decided on the basis of attitude towards risk, personal risk and probability that the risk of decision being wrong.
(ii) Decision Tree:
Decision tree is one of the best ways to analyze a decision. These are a useful way of modeling decisions that involve a progression of decisions, each with outcomes that include uncertainty.
Decision trees, in the form of a tree, depict:
(a) The decision points,
(b) Chance events, and
(c) Probabilities involved in various courses that might be undertaken.
Decision tree approach makes it possible to analyze at least the major alternatives and the fact that subsequent decisions may depend on events in the future. By assigning the probabilities of various events in the tree, managers can also comprehend the true probability of decision leading to the desired results.
(iii) Preference Theory (or Utility Theory):
This theory is based on the notion that individual attitude varies towards risk. Some persons are willing to take only smaller risks and avoid major risks, while others are willing to take greater risks. According to the preference theory, purely statistical probabilities, as applied to decision making, rest on the assumption that decision makers will follow them.
Managers avoid risk if the penalty of being wrong is severe (monetary loss, job security or reputation). Decision maker’s aversion or acceptance of risk depends upon the probability of risk and his attitude toward risk. Higher-level managers are accustomed to take larger risks. Most managers are risk averters and hence miss opportunities.
Essay # 7. Current Trends in Decision Making:
The modern approaches to decision making emphasize the process of model building, mathematical analysis and computer management decisions. Considerable progress has been made in the use of quantitative analysis for decision making.
Current trends in the field of decision making are:
i. Use of tools and models in decision making.
ii. Increasing application of behavioural science to the problem of administration decisions.
iii. Increasing use of computer applications and management information systems.
iv. Development of theories, analytical concept and models.
Essay # 8. Group Decision Making:
Group decision making is the decision making with the active participation by involving subordinates. It helps in introducing a change, enhances their sense of belongingness, and improves the environment in the organisation.
As this is an urge of the employees working in an organisation for their involvement in decision making, therefore group decision making unfreezes the fixed and formed attitude and creates a good and healthy work culture. The group develops certain standards and norms of conduct and those individuals who fail to live up to those standards are subject to pressure to conform to these standards.
Participative Management in the form of Quality circles, shop floor Councils etc. are also sort of group (collective) decision making.
A Group of persons when jointly takes a decision; the process is termed as Group decision making. The group is known as committee, broad, task force, commission or team, and the method is useful when either the problem is too large or when they concern many departments or subordinates are required to be involved in the process of decision making.
Problem and Opportunity Finding:
(A) Problem Finding:
A problem arises when an actual state of affairs differ from a desired state of affairs.
The problems may be of following types:
(i) Deviation from past experience.
(ii) Deviation from plan.
(iii) Performance of competitors.
(iv) Other people creating a problem.
(B) Opportunity Finding:
Opportunities are the situation that occurs when circumstances offer the chance to the stated goals and objectives.