Read this essay to learn about Managerial Economics. After reading this essay you will learn about:- 1. Meaning of Managerial Economics 2. Features of Managerial Economics 3. Nature 4. Importance 5. Managerial Economics and Traditional Economics 6. Relation to Other Disciplines 7. Role in Decision-Making.
Essay Contents:
- Essay on the Meaning of Managerial Economics
- Essay on the Features of Managerial Economics
- Essay on the Nature of Managerial Economics
- Essay on the Importance of Managerial Economics
- Essay on Managerial Economics and Traditional Economics
- Essay on the Relation of Managerial Economics to Other Disciplines
- Essay on the Role of Managerial Economics in Decision-Making
Essay # 1. Meaning of Managerial Economics:
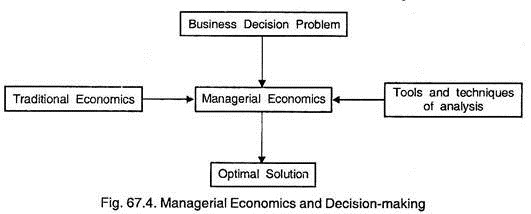
Managerial Economics is economics applied to decision-making. It is based on economic analysis for identifying problems, organising information, and evaluating alternatives. Managerial economics serve as a link between economic theories and managerial practice.
Managerial Economics is the integration of economic theory with business practice for the purpose of facilitating decision-making and forward planning by management.
Essay # 2. Features of Managerial Economics:
i. It is concerned with decision-making of economic nature.
ii. It deals with identification of economic choices and allocation of resources.
iii. It deals, as to how decisions should be taken to achieve the organisational goals.
iv. It provides a link between traditional economics and the decision sciences for managerial decision-making.
v. It is concerned with those analytical tools which are helpful in improving the decision-making.
Essay # 3. Nature of Managerial Economics:
Managerial economics is concerned with the business firms and their economic problems. To understand the nature of managerial economics better, let us study the nature of economic theory relevant for managerial decision-making.
(a) Macro-Economic Conditions:
The decisions of the firm are generally made within the broad framework of economic environment within which the firm operates. These are known as macro-economic conditions. Prom this point of view, these conditions is working of the market, pace of economic change, economic policies of the government.
(b) Micro-Economic Analysis:
This deals with the problems of an individual firm, industry etc. This helps in studying as to what is going on within the firm, how best to allocate scarce resources for various activities of the firm.
Some of the popular micro-economic concepts are the elasticity of demand, marginal cost, opportunity cost, market structure. Some of the common models used in micro-economic theory are model for monopoly price, model for price determination and the behaviour and managerial models.
Essay # 4. Importance of Managerial Economics:
Managerial economics helps the decision-making process in the following ways:
(i) It provides a number of tools and techniques. These techniques are in the form of models, which helps the manager to establish essential relationships that represent the actual situation.
(ii) It provides most of the concepts that are required for the analysis of the problems, concepts of elasticity of demand, fixed and variable costs, short and long-run costs etc., help in understanding and then solving the decision problems.
(iii) It helps in taking decisions about product-mix, level of output and price of the product, investment, how much to advertise, etc.
(iv) Managerial economics helps in taking decision on following subjects:
a. Objectives of a business firm,
b. Production and cost,
c. Profit,
d. Pricing and output,
e. Demand forecasting,
f. Competition,
g. Investment, and
h. Sales promotion and market strategy.
Essay # 5. Managerial Economics and Traditional Economics:
Managerial Economics is an applied field, whereas economics provide certain basic concepts and analytical tools. Both of them are concerned with problems of scarcity and resource allocation, generally labour and capital in order to find the best way to utilize them for achieving the set goals.
Main contributions of economics to managerial economics are:
(a) To help in understanding the market conditions and the general economic environment in which the firm is working.
(b) To provide philosophy for understanding and analysing resource allocation problems.
Success of any business depends upon technical and economic efficiency. Technical efficiency means production with best technological specifications, while economic efficiency means maximisation of its goals, i.e., sales, profit etc. Managerial economics is concerned with both kinds of efficiencies, and takes the help of economic analysis for achieving both these efficiencies.
Essay # 6. Relation of Managerial Economics to Other Disciplines:
Managerial economics has relation to number of disciplines.
Relationship with some of the important disciplines is described hereunder:
1. Statistics:
Managerial economics use statistically arrived functional relationships for decision making. It also uses theory of probability to deal with the uncertainty of future events. It also employs statistical methods for empirical testing of economic generalisations.
2. Mathematics:
Most of economic concepts, e.g., demand, price, cost, product, wages, interest, capital etc., are quantitative in nature. In economic analysis various mathematical tools and concepts like, vectors, algebra, calculus, exponentials etc., are used.
3. Accounting:
Accounting information’s are the principle sources of data required by managerial economics for its decision-making. These accounting data are provided in a form so as to fit easily into the concepts and analysis of managerial economics.
4. Psychology and Organisation Behaviour:
Managerial economics analyses the individual behaviour of micro-economic units, like a buyer, seller, an investor, a worker, and an employer. Psychology helps in understanding the behavioural aspects.
5. Operation Research:
Object of both Operation Research and Managerial economics is to take effective decisions for adopting best way of achieving firm’s objectives. The difference in both of them is that, managerial economics is a fundamental academic subject to make one understand and analyse the problems, while operation research is a functional activity carried out to help the manager to carry out his job of solving decision problems.
Operation Research is concerned with model building. Economic theory is also concerned with model building. Economic models are general and confined to broad economic decisions only, while operation research models can solve problems of various disciplines. O.R. Models, like linear programming and queuing etc., are widely used in managerial economics.
Essay # 7. Role of Managerial Economics in Decision-Making:
Main tasks of a manager are making decisions and processing information’s. For making intelligent decisions, managers must be able to obtain, process and use information. The knowledge of economic theories to a manager helps him in these functions.
Manager is required to take two types of decisions: specific decisions or general task decisions based on the information’s obtained and processed by him:
1. Specific Decisions:
These are not likely to be frequently repeated and are very important decisions and require the use of basic economics. Some of such decisions are—whether install a costly plant or get the work done from outside, whether or not to close down a branch of the firm that has recently been profitable. These include decisions related to pricing, demand forecasting, economic analysis of the industry etc.
2. General Task Decisions:
Decisions are influenced by external factors as well as internal factors. Internal factors are within control, while external factors are beyond control, but timely adjustments can be done to these external factors.
The managerial economics help in understanding these external factors, important external factors are:
i. General economic conditions like level and rate of growth of national economy, influence of international factors.
ii. Prospects of demand for the product. For example, change occurring in the purchasing power of public in general, changes undergoing in fashions, tastes and preferences.
iii. Factors influencing input cost.
iv. Market conditions for raw material and for finished product.
v. Firms share in the market.
vi. Government’s economic policies.
Internal Factors are:
i. Production, sales, inventory schedules, their present positions and forecasts for future.
ii. Pricing and profit policies.
iii. Most profitable product-mix, and the best prices for its various outputs considering the market conditions.
iv. Investment decisions, forecast about the return on investment.
Manager is required to understand both types of factors which may influence his decisions.