Are you looking for an essay on the ‘National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD)’? Find paragraphs, long and short essays on the ‘National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD)’ especially written for school and college students.
Essay on NABARD
Essay Contents:
- Essay on the Introduction to NABARD
- Essay on the Objectives of NABARD
- Essay on the Management of NABARD
- Essay on the Functions of NABARD
- Essay on the Progress of NABARD
Essay # 1. Introduction to NABARD:
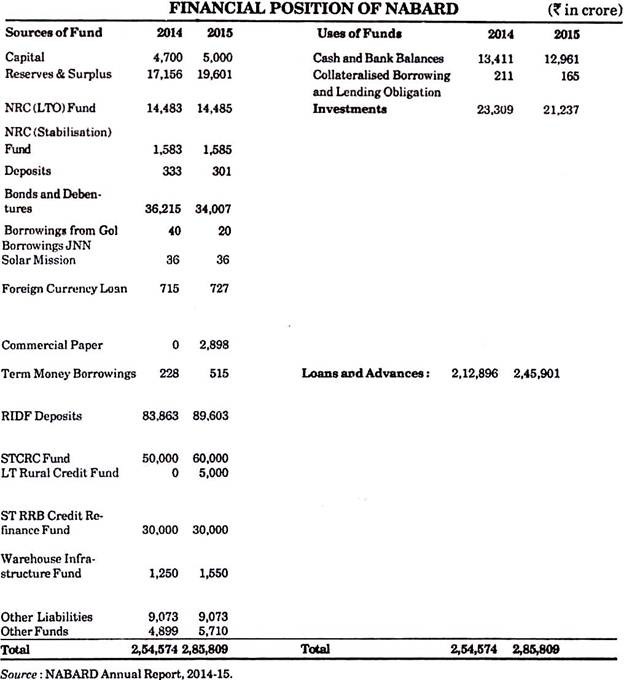
National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD) was established on 12th July, 1982 as per law. This bank was founded as an apex institute for agriculture and rural development. After NABARD’s establishment, functions of Agriculture Credit Development and Agriculture Refinance and Development Corporation of Reserve Bank were merged to this bank.
At the time of foundation, NABARD’s paid up capital was Rs. 100 cores in which contribution of Indian government and Reserve Bank were equal in the year 1996-97, it was enhanced up to Rs. 1000 crores, where contributions of Indian Government and Reserve Bank were Rs. 200 crores and Rs. 800 crores respectively.
In the central budget of 1996-97, NABARD’s Share capital was hypothecated to be enhanced upto Rs. 2000 crores by the year 1999, by adding Rs. 500 crores every year. Rs. 500 crores had already been enhanced in the year 1996-97, thus making it Rs. 1000 crores. Reserve Bank contributed Rs. 100 crores and Rs. 400 crores was the contributing share of Indian government in this enhancement. With this gradual enhancement, NABARD’s capital reached up to Rs. 2000 crores in March, 1999.
So far as financial resources of NABARD are concerned, it has the right to lift loans from the market through bonds and debentures along with the contributions of Indian government and Reserve Bank. In union budget 2011-12, it was announced that NABARD’s share capital is hypothecated to be enhanced by Rs. 3,000 crore.
Thus the share capital of NABARD reached to Rs. 5,000 crore. Cabinet of Central Government has decided in the meeting of 7 February, 2013 authorised capital of NABARD will increase to Rs. 20,000 crore in futures. For this the Act of NABARD will be amended.
On 1st April, 1995 under the premises of NABARD a new Rural Infrastructural Development Fund-RIDF was established. For this fund contribution was accepted from those banks which had failed to provide credit to the agriculture sector according to the target.
Essay # 2. Objectives of NABARD:
NABARD is an apex institution for agriculture and Rural Development.
Following are the chief objectives of its establishment:
i. To direct and determine the rural development.
ii. To financially supplement the loan-providing institutions for rural loan-system.
iii. To manage loans for the small scale industries, development of rural handicrafts.
iv. To co-ordinate all the rural loan-providing institutions.
v. To inspect, control and evaluate the projects obtaining re-finance from NABARD.
vi. To determine the policies for rural development by contacting the Indian government, Reserve Bank, State government and other policy-making institutions.
vii. To arrange for the training of bank employees to solidity the loan-imparting System.
Essay # 3. Management of NABARD:
NABARD is managed by a management board. The appointment of management board is made by the Indian Government, as per the advice of Reserve Bank, Besides the President and managing director there are two such directors who are experts in rural economics and development.
Moreover, three directors from among the Reserve Bank directors, three directors nominated Indian government and two directors from state government are included. One of the deputies Governors of Reserve Bank holds the post of Chairman of NABARD. There are 15 members in the managing committee of NABARD.
Essay # 4. Functions of NABARD:
NABARD’s main functions are follows:
1. Providing Refinance:
Resources like short term loan, Medium Term Loan and Long Term Loan are provided to different institution by NABARD.
(a) Short Term Loan:
Short term Loan’s maximum durations is of 15 months. NABARD extends loans to co-operative banks, Regional Rural Banks and other financial structures approved by the Reserve Bank, for Seasonal agricultural movements, small scale industries, handicrafts and arts, sericulture etc.
(b) Medium Term Loan:
This loan’s duration is more than 15 months but not more than 7 years. NABARD imparts loans to State Co-operative Banks, Land Development Banks, and Regional Rural Banks for agriculture and rural-development related works.
(c) Long Term Loan:
These loans are for 25 years. NABARD Provides these loans to commercial Banks, Regional Rural Banks, State Co-operative Banks and other financial institutions approved by the Reserve Bank for land development, dairy development, poultry farms, sheep rearing, pig rearing, agriculture-mechanisation, fish farming, storage, honey-bee rearing, optional sources of energy etc.
2. Developmental Functions:
NABARD performs many development al functions, too. For examples-to unite various loans-giving institutions, to help the government, Reserve Bank and other institutions in their works of rural development efforts, to make arrangement for the training of employees of regional rural banks, State Co-operative banks and land development banks etc. Besides NABARD also provides all kinds of information related to banking and rural development.
3. Regularity Functions:
NABARD also fulfills the responsibility of regularity functions. Under this function, it inspects the working method (modus operandi) of regional rural banks and Co-operative banks. When these banks desire to open a new branch, they send their application to the Reserve Bank through NABARD. NABARD holds the right to have any kind of information and detail from these banks.
4. Other Functions:
Besides the above mentioned functions, NABARD does some other functions, too. Agricultural and non-agricultural sectors are included in it. NABARD pays special attention to the problems of rural development and the needs of the weaker classes.
For this ‘Research and Development Fund’ has been established by NABARD. This helps in encouraging the research work in agriculture and in determining suitable planning for various sectors. NABARD consultancy services Pvt. Ltd. (NABCONS) has been established as wholly owned subsidiary of NABARD.
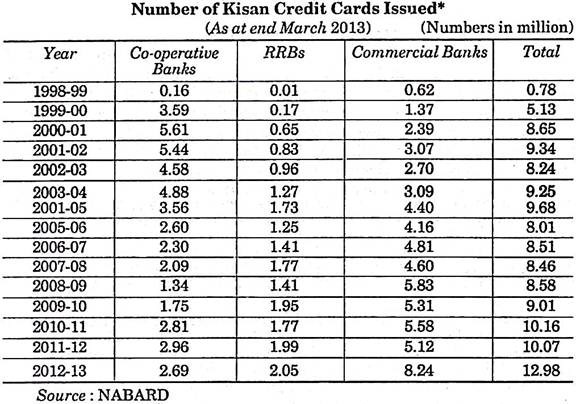
According to the amendment made in the budget of 1998-99 by Central Government, NABARD has prepared the model of Kisan Credit Card, as per the advice from Reserve Bank and other prominent banks. This project’s objective is to provide loan facility to farmers.
The details of Kisan Credit Card distributed in the last few years are clearly indicated by the following chart:
Seeing the growing demand and usefulness of micro finance, the government intends to make NABARD a Regularity Board. A bill for this purpose was presented in the Parliament. With the approval of the bill, it has become mandatory for all the institution providing microfinance to get registered with NABARD. The related institution must have a minimum amount of Rs. 5 lakh at the time of registration. As per the law, the loan amount of Rs. 50 thousand has been categorised as microfinance while in the case of house loans, Rs. 1.50 lakhs comes under it.
Essay # 5. Progress of NABARD:
There has come a change in the financial atmosphere of the country with the establishment of NABARD. It has positively attempted to lessen the regional inequalities through regional rural banks, co-operative banks and commercial banks working in country.
The progress of NABARD can be made clear by the following captions:
(1) Village Development Programme:
In the year 2007-08, Village Development Programme was implemented in 916 villages of 421 districts of 25 states of the country. The Purpose of this programme is to accelerate the speed of social and economic development in villages in such a way that the available resources may be properly used.
(2) Farm Innovation:
In the Year 2008-09,14 new proposal were accepted with the purpose to bring innovation in the fields of rural agricultural development. For this a provision of Rs. 181 lakhs was kept. With the acceptance of this new proposal, the total of proposal of this sector reached upto sixty one. Sixteen out of them have been completed.
(3) Farmer’s Technology Fund:
Farmer’s Technology Funds was started to provide information related agricultural technology to the farmers. So far, 38,215 Kisan Clubs have been established by adding 87,724 villages of 581 districts. The farmers of these clubs are provided with the knowledge of new technology in Agricultural Science Centres, Agriculture Research Institutes, Agriculture University etc. so that they may enhance their agricultural productivity.
(4) Umbrella Programme on National Resource Management:
In the year 2008-09, an amount of Rs. 451 lakh was provided for the management of natural resources in Bihar, Gujarat, Maharashtra and Tamil Nadu, from which Rs. 260 lakhs has already been allotted this year.
(5) Government Sponsored Schemes:
Various government sponsored schemes have been started by NABARD in which they have succeeded to a great extent.
The progresses of some of the important schemes are as follows:
(a) Cold Storage:
Through NABARD so far 1,578 cold storages have been established in the country’s different states with an investment of Rs. 2,76,090 lakh. Uttar Pradesh tops this list with 775 units; Gujarat holds the 2nd position with 107 units. Accordingly, 103 units in Punjab and 78 units in Bihar have been established. Rs. 41,234 lakhs has been accepted as yet for the payment to the entrepreneurs of these units.
(b) Rural Godowns:
The building of Rural Godowns has been developed for the projection of farmers’ produce. So far with the help of NABARD and through different entrepreneurs 13,019 rural godowns have been constructed in the country by investing Rs. 2,47,686 lakh. For this 35,508 lakh has been provided as subsidy too. Gujarat has the maximum numbers of godowns of this kind which are used regularly.
Accordingly, 1913 rural godown in Karnataka, 1,214 in Punjab, 773 in Andhra Pradesh, 555 in Rajasthan, 2,565 in West Bengal, 296 in Haryana, 231 in Chhattisgarh, 259 in Orissa, 209 in U.P., 164 in Assam, 43 in Bihar and 88 in Uttrakhand have been brought in existence.
(c) Onion Godowns:
Rs. 988 lakh has been released so far for construction of 213 godowns for the storage of onions in the country’s four onion-producing states-Gujarat, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra and Uttar Pradesh. The total capacity of these godowns for storing onion is 34,691 tons.
NABARD has also displayed a remarkable progress in the fields of development of dairies, animal husbandry, marketing, etc.